Ferritin in Serum
The most sensitive marker of iron storage and also an indicator of inflammation.
Also known as:
S-ferritin
.Do not confuse with serum Iron (Fe).
Video explainer of this page
Ferritin ranges for
Interpret your result
"Normal" lab range for Ferritin is between 22 and 500 µg/L for males:
0
22
500
Symptomatic hemochromatosis was associated with Ferritin above 500 µg/L:
0
500
Unexplained fatigue and weakness was associated with Ferritin below 50 µg/L:
0
50
Hair loss was associated with Ferritin below 40 µg/L:
0
40
70
Restless Legs Syndrome was associated with Ferritin below 75 µg/L:
0
75
Increased all cause mortality was associated with Ferritin above 194 µg/L in males:
0
194
Optimal range
Optimal range for Ferritin seems to be between 60 and 110 µg/L:
0
40
60
110
200
This isn’t medical advice. Consult your healthcare provider.
Possible reasons for low Ferritin:
Possible consequences from low Ferritin:
- Hair lossIn a meta-analysis of 36 observational studies, the average ferritin levels in patients with hair loss were 20.65 ng/dL lower than those in controls (childbearing age women). The meta-analysis concludes "Women with hair loss can benefit from higher ferritin levels."In a smaller study involving 210 patients with hair loss and 210 healthy controls, females with hair loss had an average ferritin level of 49.27 µg/L, while healthy women had an average of 77.89 µg/L. Additionally, 22.7% of males with hair loss had a serum ferritin level lower than 70 µg/L, compared to healthy males, where non of them had ferritin levels below 70 µg/L.
How to increase Ferritin:
- American Gastroenterological Association recommends the following for patients with anemia and ferritin below 45 ng/mL:
- Adult men and postmenopausal women: Strongly recommends bidirectional endoscopy before initiating iron supplementation.
- Premenopausal women, vegetarians and frequent blood donors: Prefers bidirectional endoscopy, but allows for non-invasive testing for H. pylori and celiac disease. - Consider the "gentle iron" supplement. Compared with other iron supplements, supplementation with ferrous bisglycinate for 4-20 weeks resulted in higher hemoglobin concentrations and fewer reported GI adverse events.Adding 500 mg of vitamin C doubles the iron absorption from FeAC (15% vs 34%) and is dose dependent. Vitamin C has to be taken at the same time as the iron supplement.,Liquid iron might not be the best first option, as it can stain the teeth.Lab check ferritin at least twice a year, since high values are dangerous."Slow-release" or "enteric-coated" Iron supplements are ineffective. Iron absorption primarily occurs in the duodenum, meaning there is only a limited window for efficient uptake.
Images:
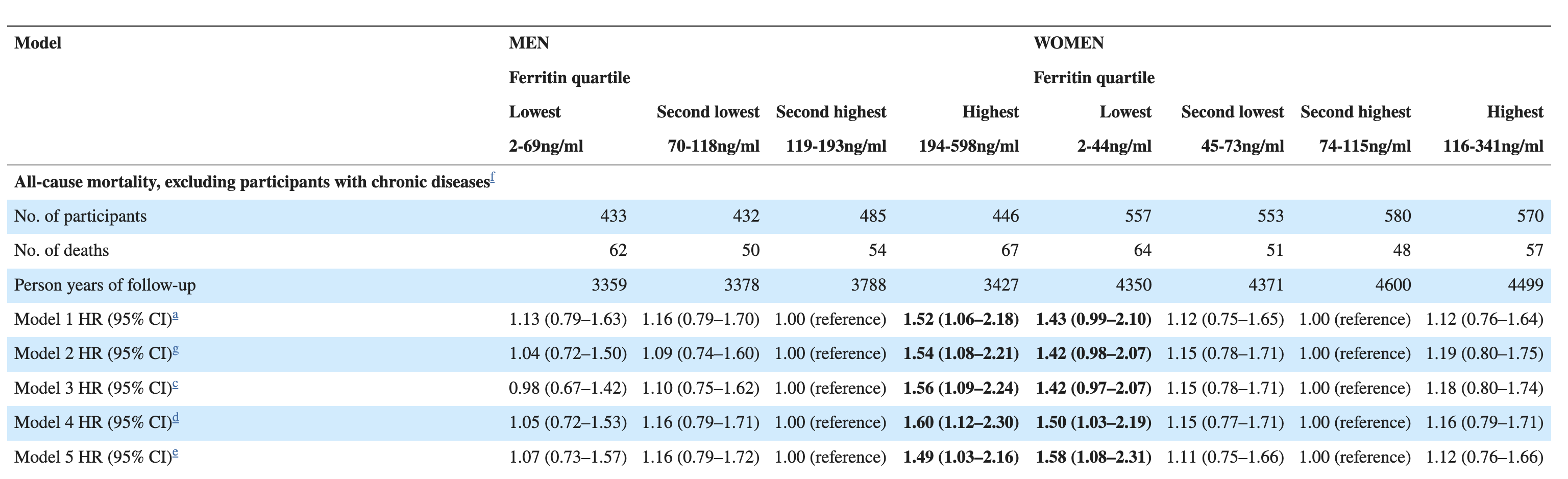
Ferritin was associated with all cause mortality
Model 5 is the fully adjusted model. Significant results in bold
5,471 participants
Community dwellers aged ≥52 years from England.
Dataset: English Longitudinal Study of Ageing
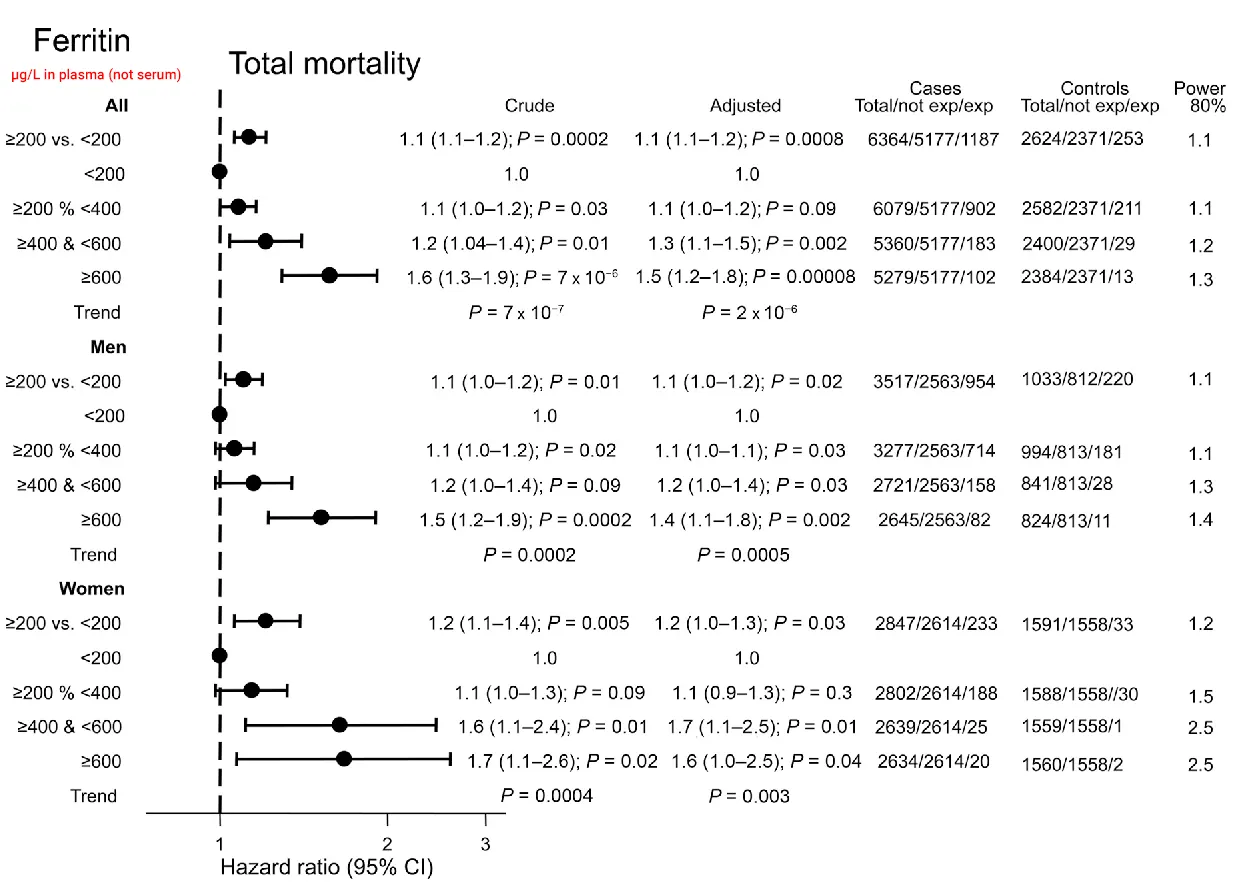
High ferritin was associated with moderate rise in mortality
Plasma ferritin cannot be reliably converted to serum ferritin.
8,988 participants
Randomly selected Danish population 20 to 80 years old followed up for 23 years.
Dataset: The Copenhagen City Heart Study
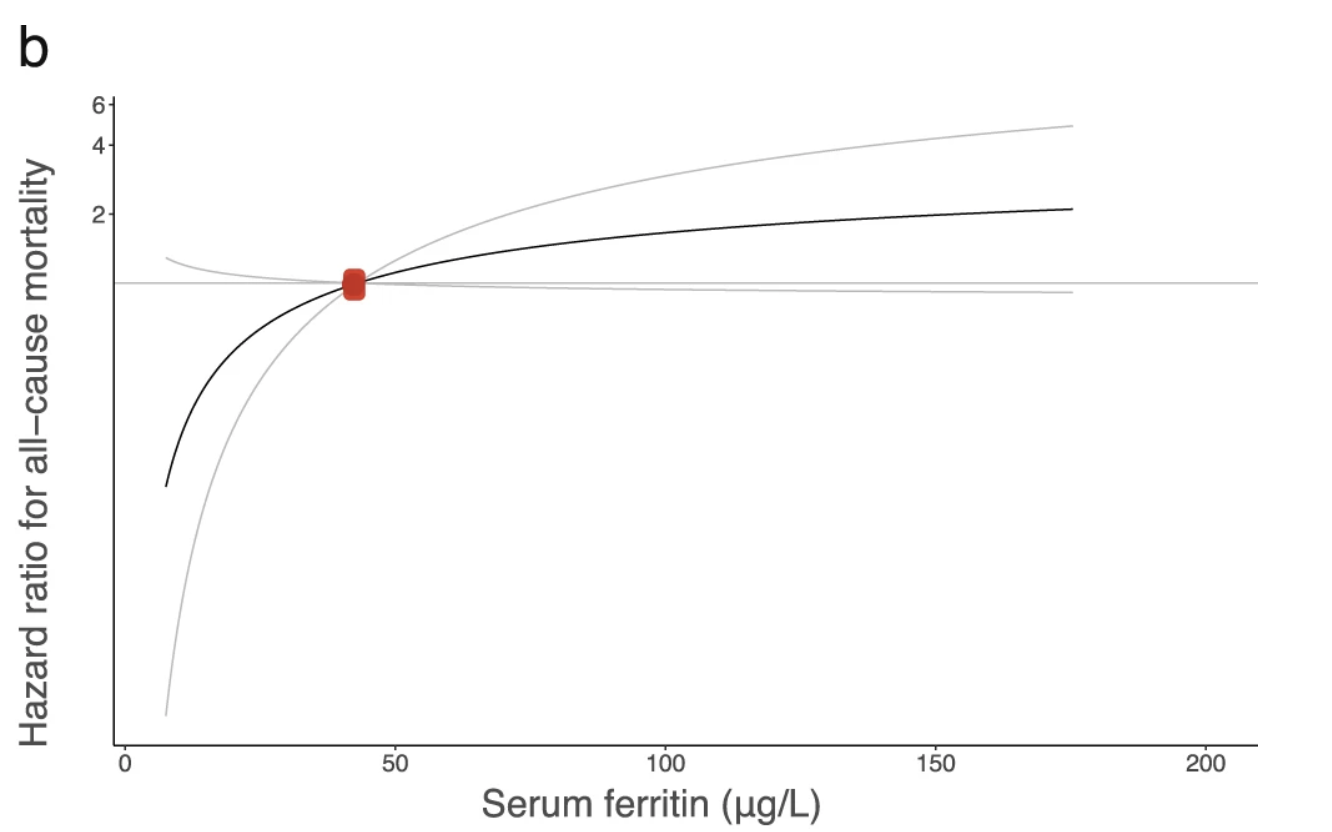
High ferritin was associated with moderate rise in mortality
257,953 participants
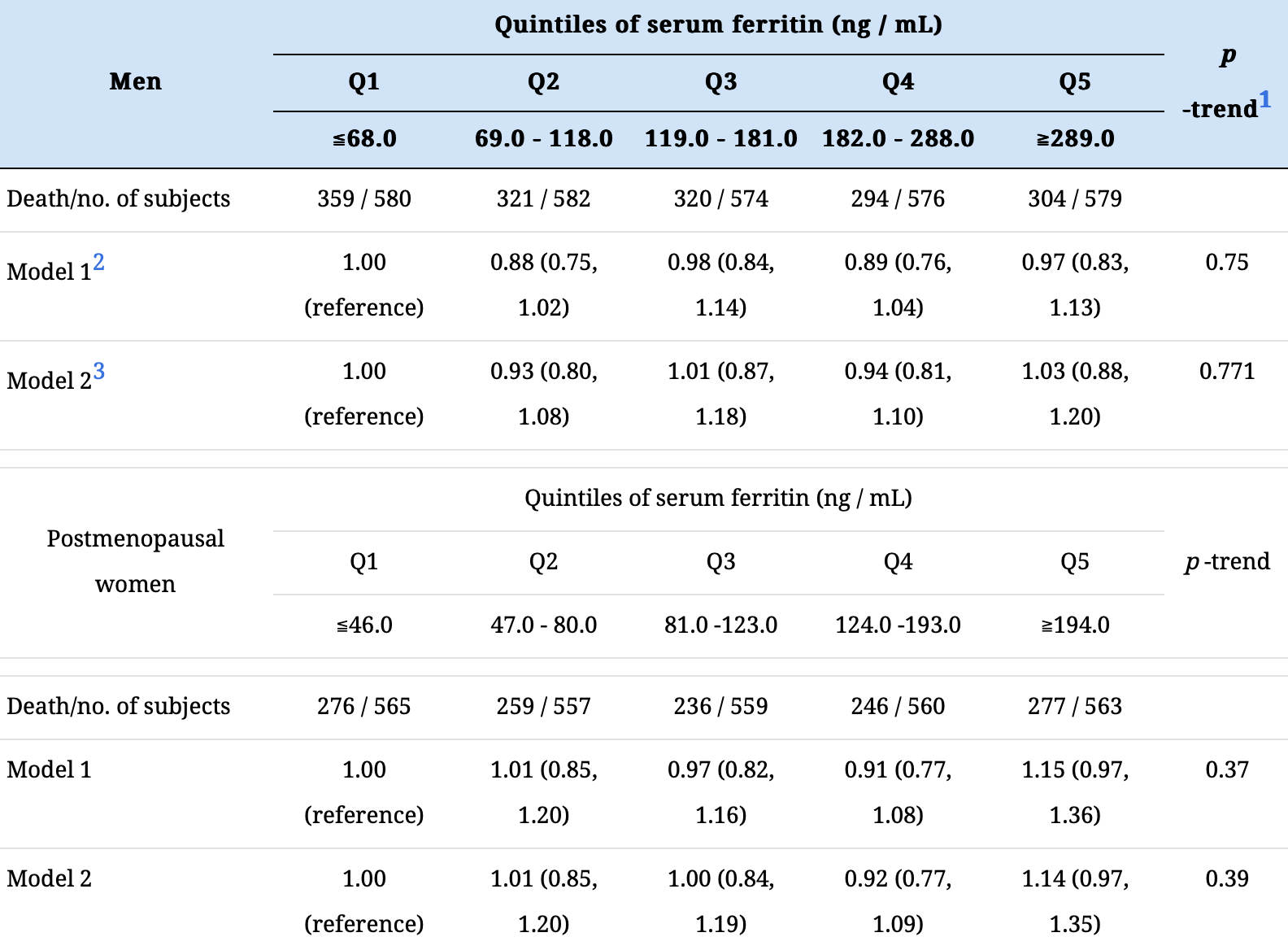
Ferritin was not associated with all-cause mortality
However, all-cause mortality was inversely associated with transferrin saturation (%) in men.
5,695 participants
50 years or older men and postmenopausal women.

About the site author
My personal mission is to extend human lifespan by collectively adding 1 million years to people's lives.
Zsolt SzaboSoftware Engineer, Biohacker, and Consultant for Longevity Clinics.
Please send me studies and feedback.
Any feedback is welcome at .
I am particularly interested in research on biomarkers linked to all-cause mortality or optimal reference ranges.